Read latest industry news
Create an account to access browse by topic and date
and get weekly news digest
Topics
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Canadian Solar profit drops 92% in Q1

Canadian Solar said its first-quarter profit for 2025 fell 91.83% year over year to CNY 47.26 million ($6.58 million), as revenue dropped 10.54% to CNY 8.586 billion amid declining margins across core business lines. Module shipments rose 9.4% to 6.9 GW. Its energy storage unit, e-STORAGE, posted a record 91 GWh in contracted backlog, with an estimated order value of $3.2 billion. Recurrent Energy, the company’s energy development unit, now holds a global project pipeline of 27 GW in solar and 76 GWh in battery storage. Canadian Solar forecast second-quarter revenue between $1.9 billion and $2.1 billion , with gross margins of 23% to 25%, module shipments of 7.5 GW to 8.0 GW, and energy storage system deliveries of 2.4 GWh to 2.6 GWh.
CEEC said the Shanghai Stock Exchange has approved its application for a targeted A-share issuance. The company plans to raise up to CNY 15.00 billion, including issuance costs, to fund large-scale energy base projects and replenish CNY 4.5 billion in working capital.
The China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association (CNMIA) said China’s silicon market softened further last week, with n-type rod silicon trading at CNY 36,000/ton to CNY 41,000/ton and averaging CNY 38,600, down 1.53% week on week. N-type granular silicon held steady at an average of CNY 36,000 , while p-type polysilicon fell 3.10% to CNY 31,300. April polysilicon output totaled 99,100 tons, a 6.08% drop from March. Wafer prices continued to decline on weak demand and low utilization. N-type G10L wafers (182 mm × 183.75 mm, 130 μm) averaged CNY 0.95, down 5.94%; n-type G12R (182 mm × 210 mm) fell 1.79% to CNY 1.10; and G12 wafers (210 mm × 210 mm) dropped 3.70% to CNY 1.30). With most wafer plants running minimal capacity and spot prices already below cost, the CNMIA said further downside appears limited.
Vanda RE has signed a 1 GW framework supply agreement with Longi for a solar-and-storage project in Indonesia’s Riau Islands. The joint venture between Gurīn Energy and Gentari said Longi will supply high-performance PV modules that meet local content requirements. The 2 GWp solar and 4.4 GWh storage project forms part of an Indonesia-Singapore green economic corridor aimed at strengthening clean tech supply chains, lowering renewable energy costs, and positioning Indonesia as a regional green energy hub. Leaders from both sides said the collaboration will support local growth, cross-border cooperation, and decarbonization efforts across the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Popular content
French startup offers solar carports made of aluminum
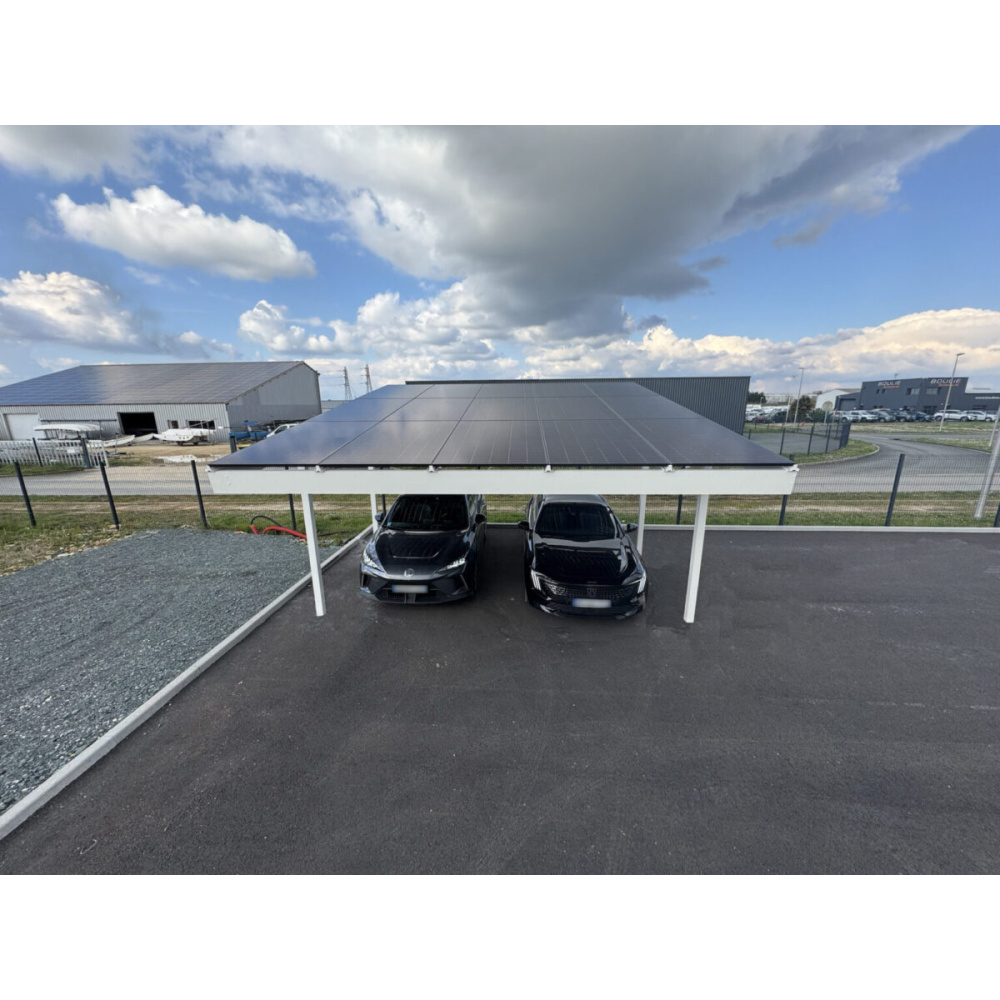

Since the Climate and Resilience Act came into effect in France in 2021, followed by the APER Act in 2023, all outdoor parking lots over 1,500 square meters must be equipped with photovoltaic canopies covering at least 50% of their surface area between 2026 and 2028. To meet this legal requirement, Closura, based in Le Thou in southwestern France, offers a range of custom-made solar canopies, ready to install or in a plug-and-play version. Their unique feature lies in the material used for their construction: marine-grade aluminum, renowned for its durability and lightness.
Developed for parking lot operators, local authorities and large commercial sites, Closura canopies, 100% made in France, combine strength, aesthetics (RAL 7016 or RAL 9010 frosted as standard), and performance. With a power output of up to 7.5 kWp depending on the carport's dimensions, their modularity also allows for optimized installation based on parking layouts.
Guaranteed for 25 years, the aluminum structure of the carport rests on four 110 mm cross-section posts, with two possible installation methods: direct anchoring or reinforced plates. The roof slope is optimized (from 5 to 10 degrees) for improved production efficiency. Optional features include the removal of corner posts, an electric vehicle charging socket, an energy monitoring gateway, the integration of rainwater gutters and an aluminum enclosure screen.
Popular content
‘There’s no need to mimic male counterparts or fit outdated stereotypes’

I believe the solar-plus industries offer an extraordinary opportunity to cultivate equity, diversity, and inclusion. As active participants in the energy transition, we are uniquely positioned to align with a generation prioritizing humanity, transparency, and authenticity. This industry's growth represents a pivotal chance to redefine leadership, attracting talent that deeply values inclusive, equitable, and transparent work environments.
Throughout my career, I've frequently encountered the stereotype that women are insufficiently assertive leaders. This perception often arises from a fundamental misunderstanding of collaborative and inclusive leadership styles. I have consistently prioritized a team-oriented approach, involving everyone in the decision-making process and fostering shared responsibility. While some interpret this as a lack of assertiveness or ambition, I see it as the embodiment of genuine leadership—empowering others and ensuring each team member feels valued and heard. By continuously highlighting the collective successes we achieve through collaboration, I've demonstrated that leadership isn't about dominance, but about guiding the group towards common goals.
Authenticity and vulnerability are essential facets of my leadership philosophy. Working in a global company Equans with 90,000 employees, I have learned that transparency is key. I actively share our goals, challenges, and progress, building trust and alignment within the team. Trust is, in fact, the cornerstone of effective leadership. By openly admitting when I don't have all the answers, I create a supportive atmosphere where colleagues feel encouraged to contribute their expertise, sparking innovation and strengthening team dynamics. Collaboration, fueled by authenticity, enables us to harness our collective intelligence and achieve exceptional outcomes.
An insight shared during a recent discussion at a WiSEu Network meeting deeply resonated with me—a woman shared her experience of leaving a company whose values conflicted with hers, and bravely founding her own venture. Her story profoundly impacted me, underscoring the courage required to remain true to one's core values. This reinforced my belief that authenticity in leadership is not merely beneficial but essential.
Reflecting on my experiences, I've identified a superpower within myself: the strength derived from collaborative leadership. Despite persistent stereotypes, being team-oriented is a powerful leadership approach. Recognizing this strength has deepened my confidence and commitment to empowering and guiding others toward collective success.
Supporting the next generation of women leaders is paramount, and we must encourage them to embrace their uniqueness rather than to conform to traditional leadership molds. There's no need for them to mimic male counterparts or fit outdated stereotypes. Instead, we should champion authenticity and individuality, viewing differences as strengths rather than liabilities. Participating in initiatives like “Educate the Girls, Educate the World” reinforced my belief in the transformative power of mentorship and education, crucial for empowering young women globally.
Christelle Mirailles is a dedicated leader known for her collaborative and authentic approach. At 44, she successfully balances her roles as a mother of three and a professional with international experience, having lived in three different countries. After graduating as an engineer in France, she started in the automotive sector, then moved to construction, nuclear, and renewable energy industries, specializing in business development. Christelle strongly believes in teamwork, actively creating environments where everyone feels valued and involved. Passionate about sustainability, she proudly contributes to the global energy transition at Equans Solar & Storage. Outside of work, Christelle enjoys music, sports, and mountain hiking. She is also actively engaged in community associations, driven by her commitment to solidarity and social responsibility.
Interested in joining Christelle Mirailles and other women industry leaders and experts at Women in Solar+ Europe? Find out more: www.wiseu.network
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content
Research project examines PV-supported charging infrastructure for electric buses

The acronym EMOSYN stands for “Electromobility, Smart Grid and Self-Generation.” Under this heading, a research team from Kiel University of Applied Sciences has been supporting the Pinneberg District Transport Company (KViP) for almost four years in the electrification of part of its bus fleet and assisted the company in the design, commissioning, optimization, and scaling of a pilot plant at its depot in Uetersen, Schleswig-Holstein.
A total of 100 kW of photovoltaic power was installed on the depot's administration building and maintenance hall. A battery storage system with a capacity of 328 kilowatt hours was housed in a container on the site. At the start of the project, a 50 kW charging station connected to the battery storage system was in operation, explained Klaus Lebert, a professor at the department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering at Kiel University's Institute of Mechatronics. A second charging station near the storage system went into operation in the second half of 2024.
The research project, supported by the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure with around €312,000 ($349,257) – of which around €154,000 went to the university – has now been completed, and the evaluation was submitted at the beginning of this year. For the Kiel University of Applied Sciences, however, the project is seen as the potential beginning of a more far-reaching plan: “The development of the energy supply infrastructure for the electrification of depots and bus fleets is quite complicated and associated with financial and logistical challenges,” said Lebert. The pilot project has now produced “a model that can serve as a kind of blueprint for other small and medium-sized public transport providers to implement a similar approach.”
The project investigated how energy generated by photovoltaics can reduce the use of grid electricity and thus contribute to cost reduction. Modeling, simulation runs, and continuous comparison with real-time data have resulted in “a highly accurate overall model for the depot.” This enabled charging strategies to be evaluated and concrete recommendations to be developed.
KViP intends to continue to utilize the findings. “We now know the relevant technical, operational, and economic parameters for integrating our own renewable energy generation into our electrification strategy,” said managing director Thomas Becker. In addition to the self-generated stations, the company now operates five additional 120 kW stations, which are currently powered by grid electricity. Twenty-seven more are to follow shortly, which will be necessary: 27 electric buses have been ordered and are scheduled to be integrated into the KViP fleet starting in late summer.
Popular content
Electric cars and heat pumps can help avoid 110 hours of negative electricity prices annually

On behalf of green energy cooperative Green Planet Energy, consulting firm Enervis investigated the potential effects of heat pumps and electric cars on electricity prices, CO₂ reductions, and the use of renewable energy sources. The study, “Flexible Use of Heat Pumps and Electric Vehicles – Analysis of Energy Economic Benefits,” concludes that targeted operational control, oriented, among other things, towards dynamic electricity tariffs, can make “the energy transition more efficient overall and electricity more affordable for everyone,” according to Carolin Dähling, head of policy and communications at Green Planet Energy.
The study analyzes and quantifies the well-known effects of using cars and heat pumps for increased flexibility in the electricity grid. Energy consumption would be deliberately shifted from the usual morning and evening peak hours to midday. A statement from Green Planet Energy states that there are no disadvantages for the affected households: “Intelligent controls ensure that the heat pumps preheat, for example, via buffer storage.” For electric cars, it is possible to specify the time by which their batteries should be charged.
The study identifies concrete achievable results of such an approach: The number of hours with negative electricity prices could be reduced by an average of 110 per year between 2025 and 2035, with corresponding effects on the profitability of wind and photovoltaic systems. The amount of energy lost due to shutdowns could be reduced by six terawatt hours per year, “and the use of expensive, climate-damaging natural gas power plants would also decrease.”
These factors would also impact electricity prices on the exchange. According to the study, consumption flexibility can reduce base load prices by €3.60 per megawatt hour and peak prices by €6.20 per megawatt hour, i.e., by 0.36 and 0.62 cents per kilowatt hour, respectively. The average day-ahead spread, i.e., the difference between the highest and lowest prices, will therefore decrease by around €20 per megawatt hour. The study estimates the CO2 savings achievable through the reduced use of gas-fired power plants at 0.7 million tons per year.
Popular content
India plans 50 MW floating solar plant at nuclear site

State-run NPCIL has contacted Ciel & Terre about building a floating solar plant at its Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP 1&2) in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu, India.
The selected site is a seawater dyke, a shallow reservoir in nuclear power plants that separates inlet water from heated water discharged after cooling the steam condenser.
Ciel & Terre estimated the site’s floating solar potential at around 50 MW.
Popular content
‘Cybersecurity is a real problem, but the Reuters report should be taken with a grain of salt”

The bombshell broke on Wednesday: A Reuters report said unexplained communication devices had been found inside some inverters and energy storage batteries made in China, and US energy officials were reportedly “reassessing the risk posed by Chinese-made devices, according to two anonymous sources.” The report did not name the manufacturers or the number of devices investigated.
“It's clear that the issue of cybersecurity is a real and worrying problem, but this information [in the Reuters report] should be taken with a grain of salt,” Garikoitz Sarriegi, senior project manager at Kiwa PI Berlin Ibérica, told pv magazine. Sarriegi states that, citing the fact that those involved in the “investigation” declined to provide further information, there is no mention of who the manufacturer is, whether multiple manufacturers are involved, or how many units with this problem they have found.
Martin Schachinger, founder of the pvXchange platform and who writes a monthly column in pv magazine on the development of the European PV market, expressed his opinion on the report on LinkedIn: “Unfortunately, the information is still very scarce and superficial. I'm eager to know if more details will be released at some point or if this will be a smokescreen that will further fuel existing conspiracy theories.”
Another point Reuters makes in its article is the ban that the United States government plans to impose starting in 2027 on several of the largest Chinese battery energy storage (BESS) manufacturers due to their close ties to the Communist Party. Several US utility companies fear that, following Huawei's ban, other Chinese inverter manufacturers could face a similar ban. “At Kiwa PI Berlin, we are talking with the largest BESS manufacturers and have verified that several of the smaller players involved use cells from these manufacturers that could be subject to the ban, so these other manufacturers would also be excluded. Given the market share of Chinese manufacturers, we find it difficult to believe that the ban will have any effect unless policies regarding this issue change drastically,” Sarriegi added.
Regarding “backdoor access,” several major Spanish engineering firms have confirmed to the consultancy firm that “they do not install any components not declared in the bill of materials (BOM) and that, without the client's permission, they cannot do anything” — such as updating parameters, modifying firmware, or turning the inverter on or off.
“What's more, it seems that they have occasionally had problems because the client has not granted them access or has been slow to do so,” Sarriegi explained. These Spanish inverter manufacturers can shut down their equipment remotely. “It's something that can be done for security reasons, always with the client's permission. I'm sure that if we ask any other European manufacturer, the answer will be the same,” he added.
Sarriegi affirmed that, in theory, when the equipment is certified, it is ensured that “everything is okay, but firmware updates are usually performed through remote access, and those don't necessarily have to be certified. That's where things can slip in. But you have to be very sure and provide truthful information before dropping such a bombshell.”
Popular content
High pressure brings solar surge to northwestern Europe
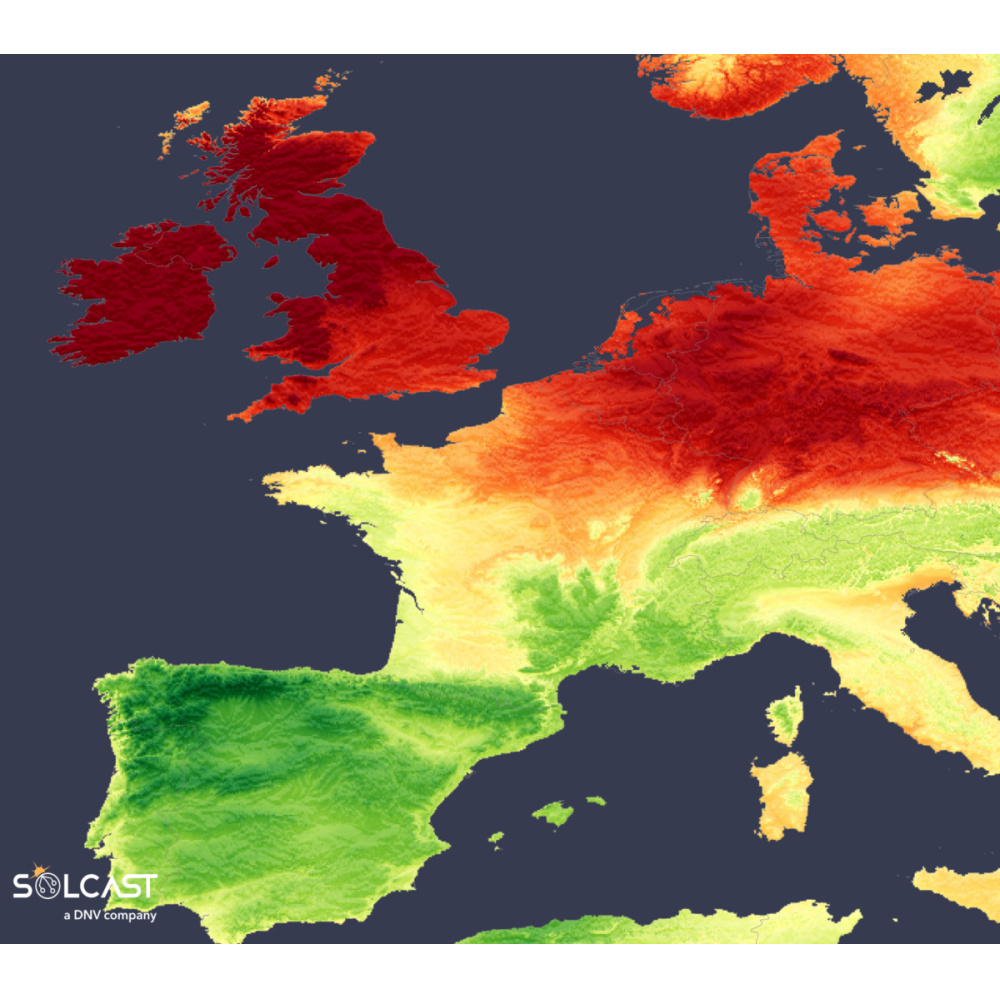
The British Isles have enjoyed an unusually bright start to May, with some areas seeing even higher irradiance than sites in Spain, according to analysis using the Solcast API. A persistent high pressure system over the North Atlantic has driven clear skies and hot temperatures across northwestern Europe, while stormy, moisture-laden systems have weighed down solar performance across the Iberian Peninsula.
During the first half of May, irradiance levels in the British Isles reached up to 35% above the norm, continuing an exceptional run of solar-friendly weather. The Netherlands, Belgium and Germany each recorded irradiance levels around 25% above average. This burst of sunshine has been linked to a stable high pressure system over the Atlantic, which has delivered dry easterly winds from continental Europe, suppressing cloud formation across the region. In London, temperatures peaked at a monthly record of 29°C on May 1.
The high irradiances observed over the British Isles in May follow on from extreme conditions in April and are a continuation of the effects of persistent high pressure. Irradiance during April was significantly above average, with the south of England recording levels 20% above the long-term mean. The UK Met Office declared it the sunniest April since records began in 1910. This prolonged sunny weather was driven by a persistent ridge of high pressure, which contributed to both elevated irradiance and unusually hot conditions throughout the region.
While northern Europe basked in sun, the Iberian Peninsula faced a far less favourable pattern for PV generation. Southern Europe experienced cloudy, storm-filled conditions that substantially reduced irradiance. By mid-May, irradiance levels were down around 20% across much of Spain and Portugal, as well as southern France.
Dublin, typically far behind Madrid in terms of solar generation, has seen more irradiance (94.69 kWh/m²) than the Spanish capital (87.48 kWh/m²) up to May 15. This inversion of typical solar patterns is striking; as you can see in the above, this is an anomaly from recent years, with conditions in Ireland approaching ‘normal Spanish weather’. To highlight the scale of this anomaly, in an average year, Madrid would have registered around 100.25 kWh/m², well ahead of Dublin's 70.33 kWh/m².
These poor conditions were driven by an enhanced jet stream that allowed anomalous low pressure systems to impact southwestern Europe. Combined with moist air masses from the south, this resulted in outbreaks of thunderstorms and heavy rain. Some regions in Spain and France also reported large hailstones, raising concerns about potential damage to solar installations and related infrastructure.
Solcast produces these figures by tracking clouds and aerosols at 1-2km resolution globally, using satellite data and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This data is used to drive irradiance models, enabling Solcast to calculate irradiance at high resolution, with typical bias of less than 2%, and also cloud-tracking forecasts. This data is used by more than 350 companies managing over 300 GW of solar assets globally.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content
UK investors back 50 MW of solar in Nigeria with $3.6 million

UK energy developer Konexa, investment manager Climate Fund Managers (CFM), and Norwegian development finance institution Norfund have signed a development funding agreement in Nigeria.
The agreement will see the development of a new 50 MW solar plant alongside new and strengthened grid infrastructure that will connect two sites belonging to Nigerian Breweries.
The partners are jointly investing $3.6 million. CFM’s EU-supported blended finance facility Climate Investor One will contribute 50%, while Norfund and Konexa will contribute 25% each to the total.
According to a statement from Konexa, the commitments are expected to unlock approximately $80 million in further investments for construction at financial close, expected during the second half of this year.
The new project will also support Konexa’s continued rollout of a private renewable energy trading platform to a broader base of commercial and industrial clients in Nigeria.
“The European Union’s early support helped unlock private capital for the first phase of the project, and we expect Norfund’s catalytic funding to do the same for the next phases,” said Darron Johnson, CFM regional head of Africa. “It’s a clear example of how blended finance can deliver impact at scale in emerging markets like Nigeria, where access to electricity remains a critical issue.”
In March, Nigeria’s Rural Electrification Agency entered into an agreement with Lagos-based renewables developer Oando Clean Energy for a 1.2 GW solar assembly plant.
Popular content
Middle East, Southeast Asia wafer makers ramp capacity amid record-low prices
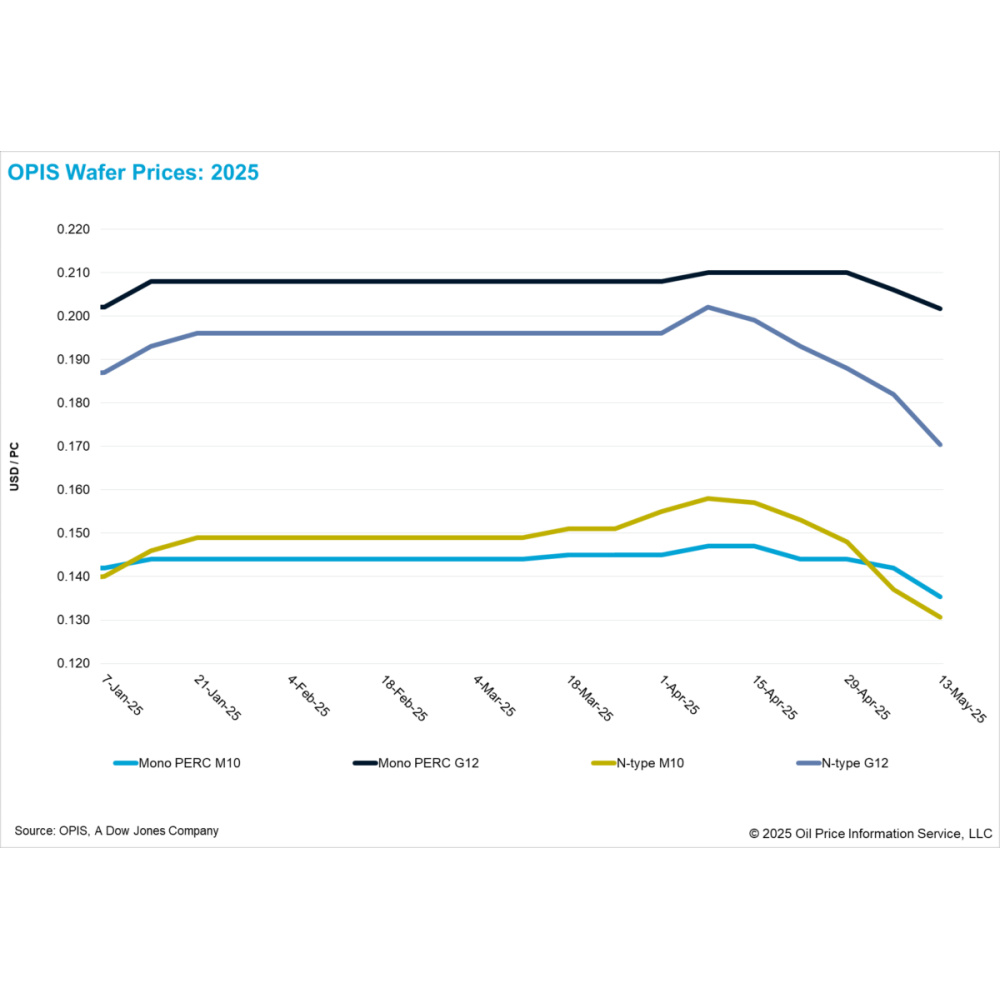
FOB China wafer prices saw broad-based declines this week. Mono PERC M10 and G12 wafer prices decreased to $0.135/pc (per piece) and $0.202/pc, representing week-on-week drops of 4.93% and 1.94%, respectively. Likewise, N-type M10 and G12 wafer prices fell to $0.131/pc and $0.170/pc, down 4.38% and 6.59% from the previous week.
The notable decline in wafer prices is largely driven by weakening downstream demand following a recent peak. Market sources indicate that both solar cell and module producers plan to reduce operating rates starting in May, with wafer manufacturers reportedly following suit.
According to insiders, specialized wafer manufacturers are maintaining relatively higher utilization rates, with one leading player reportedly operating at around 80% capacity. In contrast, integrated manufacturers have reduced their utilization to approximately 55%, while smaller second- and third-tier producers, constrained by limited capacity and outdated equipment, are running at just 20% to 30%.
Although current wafer inventories remain manageable, weakening demand combined with persistent overcapacity has heightened the risk of inventory accumulation. In response, some wafer manufacturers have begun reducing prices and are sacrificing profit margins in an effort to stimulate sales, according to trade sources. The prevailing transaction price for mainstream N-type M10 and 182*183 mm wafers in the Chinese market reportedly hovers around CNY 1 ($0.14)/pc, with certain 182*183 mm wafers already trading below this threshold. Industry sources report that some cell manufacturers are insisting on a maximum wafer procurement price of CNY 1/pc.
Concerns are mounting over the future profitability of wafer manufacturers. One market observer noted that, under ideal conditions – full production capacity and access to N-type polysilicon priced below CNY 30/kg – the cash production cost for N-type M10 wafers could be limited to around CNY 1/pc. However, with current N-type polysilicon prices remaining in the higher range of CNY 30/kg to CNY 40/kg, and wafer production lines operating below optimal levels, financial losses across the sector are becoming increasingly apparent.
Looking ahead, widespread pessimism surrounding market demand in 2025 is deepening bearish sentiment regarding the profitability outlook for Chinese wafer producers. Industry insiders point out that, due to the sector’s vast capacity and high operational flexibility, any meaningful capacity reduction will likely be a prolonged process. In the interim, the ability to maintain sufficient cash flow will be critical for determining whether companies can endure in the long term.
In the global market, operational trends among wafer manufacturers outside China are showing mixed developments. A Southeast Asian wafer producer with an estimated capacity of 6 GW is reportedly increasing its operating rate from below 50% to over 70% in May, driven by the rapid expansion of cell manufacturing facilities in Indonesia. In contrast, another Southeast Asian wafer manufacturer of similar capacity is said to be maintaining a relatively low utilization rate of around 30%.
Meanwhile, a company that has announced large-scale wafer manufacturing plans in the Middle East is reportedly preparing to commence construction as early as the first or second quarter of next year. However, a source familiar with the matter noted that the company is still assessing the economic feasibility of the project, raising the possibility of further delays.
OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides energy prices, news, data, and analysis on gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, LPG/NGL, coal, metals, and chemicals, as well as renewable fuels and environmental commodities. It acquired pricing data assets from Singapore Solar Exchange in 2022 and now publishes the OPIS APAC Solar Weekly Report.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content
New biodiversity toolkit helps solar farm developers fast-track projects

Biodiversity offset specialist Thesium has launched a new product designed to help solar farm developers de-risk and accelerate their projects.
The Biodiversity in a Box tool is built for infrastructure and energy developers and decision makers facing complex regulatory environments by providing a structured assessment of biodiversity offset risks, and delivering a tailored offset strategy, credit feasibility analysis, and board-ready stakeholder documentation.
Thesium Principal Ecologist Greg Steenbeeke said too many developers are flying blind when it comes to biodiversity offsets.
“They engage too late, underestimate long-term stewardship costs, and suffer for it in both time and money. Biodiversity in a Box flips that script. It turns biodiversity from a liability into a competitive advantage,” Steenbeeke said.
Biodiversity in a Box addresses financial and regulatory risks associated with treating biodiversity offsets as an afterthought and aims to support project teams with navigating the intricate biodiversity credit offset demands and avoid costly delays often associated with biodiversity planning.
Thesium Strategy and Engagement Lead Paul Cubelic said the Box gives developers tools to seamlessly plan biodiversity offsets just like they plan for concrete or steel.
“This isn’t just a report, it’s a blueprint for certainty in a market that’s defined by risk,” Cubelic said.
The product includes a comprehensive offset risk assessment to reveal hidden financial risks, gaps in biodiversity planning, regulatory issues, and overlooked land management obligations and a customized offset strategy with financial modelling that includes milestone alignment with regulatory pathways, identification of scarce credit, integration timelines, and ROI.
Popular content
Rising demand for home solar storage in Switzerland
From ESS News
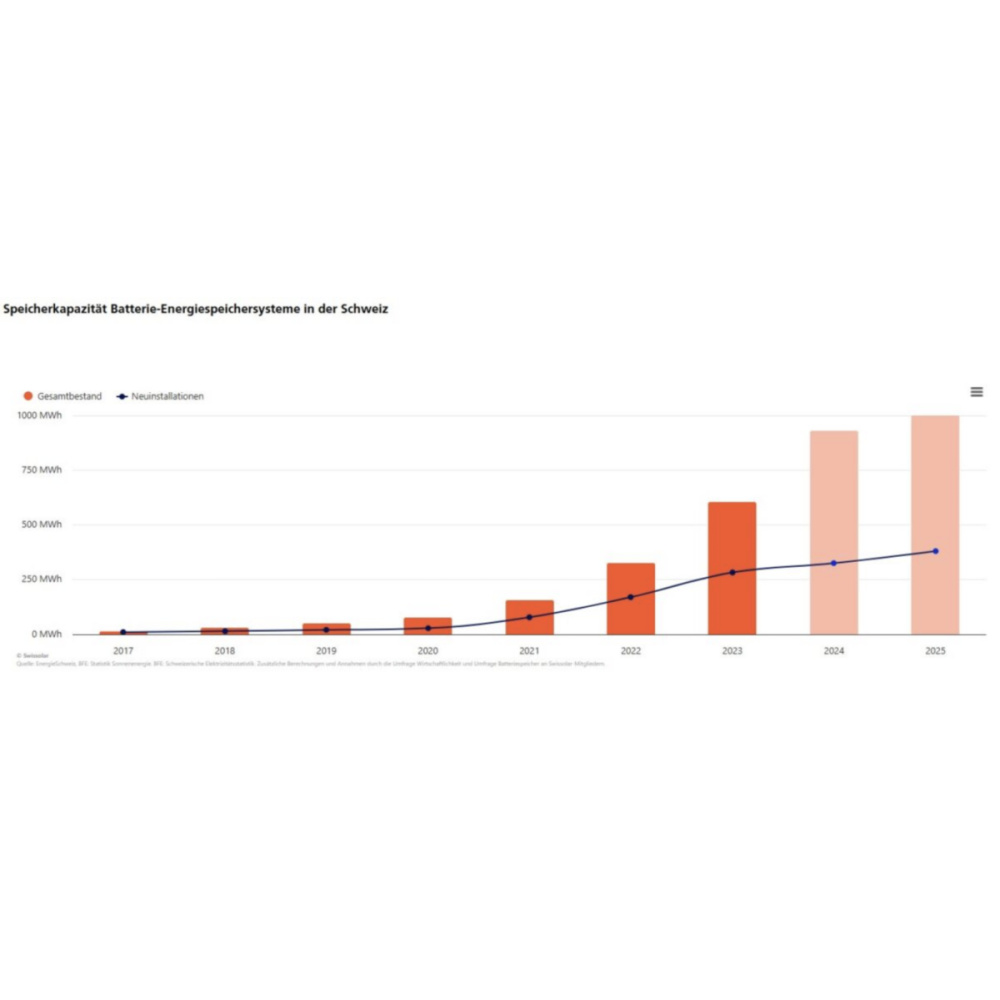
In Switzerland, roughly every second residential PV system is installed together with a battery energy storage system (BESS).
“Over the past three years, the total number of battery storage systems has doubled almost annually,” stated industry body Swissolar in its first storage market report, published at the organization’s Members’ Day, in Lucerne yesterday.
A key reason for the popularity of home energy storage is a continuing decline in equipment prices which Swissolar estimated at $115/kWh for 2024.
Popular content
Australian solar installer convicted for false claims

Following an investigation by the Clean Energy Regulator (CER), an electrician in South Australia has been convicted and fined for providing false or misleading documents in the Small-Scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES).
Liam Sheppard pleaded guilty to charges relating to 62 solar system installations. Sheppard falsely claimed to have installed or supervised these installations.
In doing so, he submitted false or misleading small-scale technology certificate assignment forms, along with certificates of electrical safety, to registered agents, who relied on the information to improperly create certificates for the installations.
On April 3, 2025, after more than three years of legal proceedings, Sheppard was convicted and received a reduced fine of AUD 3,500 ($2,250) due to his personal circumstances.
Along with reputational damage, convictions of this type can lead to loss of licenses, exclusion from industry associations, restrictions on international travel and diminished trust from clients.
Registered agents, installers and designers have significant compliance obligations under the SRES, and the CER is committed to continue to monitor and enforce the obligations to ensure scheme integrity, saying it has zero tolerance for fraud.
“Those who don’t comply with their obligations will see enforcement action taken against them where it is warranted under our compliance, education and enforcement policy,” a CER statement on the matter reads.
Popular content
Can dimethyl ether replace propane as refrigerant in heat pumps?

Researchers from Spain’s Jaume I University have tested different refrigerants that might be alternatives to propane (R290) in existing refrigeration and heat pump systems.
The scientists investigated, in particular, the performances of dimethyl ether (RE170) and ternary mixtures of carbon dioxide, dimethyl ether, and butane (R744/RE170/R600).
“The use of dimethyl ether (DME) has regained again attention during the last years, since it is a fluid with excellent thermophysical and environmental properties (low global warming potential and zero ozone depletion potential),” the scientists said. “However, although this search has been considered from a theoretical perspective as a replacement for R290, it has not yet been experimentally validated.”
The researchers started with a thermodynamic analysis of the different refrigerants using the Refprop v.10 software. Different ratios of the ternary mixtures were simulated in a simple vapor compression cycle operating at an evaporation temperature of 0 C and condensing temperature of 50 C. Superheating and subcooling values are set to 4 K and 1 K, respectively.
“Concretely, the model indicates that the alternative fluids could offer theoretical coefficient of performance for refrigeration (COPR) increments between 8.3% to 13.5% and coefficient of performance for heat pump (COPHP) increments of between 6.5% to 10.3%,” the team noted. “As the thermodynamic properties are estimated with Refprop due to the absence of adjusted binary mixing coefficients, this work has addressed the analysis using an experimental approach.”
The experiment
The experimental approach considered R290 and RE170 as pure fluids and 11 blends composed of different proportions of RE170/R600/R744. They were tested in an experimental plant that was adapted for the use of R290. The plant is described as a water-to-water single-stage vapor compression cycle with an electronic expansion valve (EXV).
“Condenser and evaporator, built in our lab, are concentric tube-in-tube heat exchangers with the refrigerant flowing through the inner tube and the secondary fluid through the annular space,” the academics said. “These heat exchangers are divided into steps to measure the temperature evolution of the refrigerant along the heat exchanger and to guarantee an accurate thermal measurement in the secondary fluid.”
All pure fluids and blends were tested using three approaches: in the drop-in test, R290 was swapped for the new refrigerant without changing the system settings. That is, keeping the test plant with the compressor speed of 2,100 rpm; in the fixed cooling capacity test, the compressor speed was adjusted for the new fluids to have the same cooling power as R290; and in the fixed heating capacity test, it was adjusted for the same heating power as R290.
The results
According to the results, nearly all the mixtures and RE170 offer higher coefficient of performance (COP) values for heating and refrigeration than R290, while also suffering large reductions in capacity. “In the drop in tests, RE170 offered COP increments in relation to R290 of 29.8% (COPR) and 17.99% (COPHP) with capacity reductions of 17.3% and 24.7%, respectively. In this test, mixture RE170/R600 (92.5/7.5) obtained a 22.8% increase in COPR and a 21.1% increase in COPHP, also with a loss of capacity,” they said.
“When the fluids were tested under the fixed cooling capacity scenario, the increments in COPs were reduced. RE170 offered 12.7% COPR and 8.4% COPHP increments with similar values for the mixture RE170/R600 (92.5/7.5). In this case, the compressor speed needed to increase >30%,” they added. “At the fixed heating capacity scenario, again the best fluid was RE170 with COP increments in relation to R290 of 12.8 % (COPR) and 5.1 % (COPHP) with compressor speeds higher up to 41%. Some mixtures offered similar results.”
Concluding their results, the academics added that the use of pure RE170 is recommended as the best overall alternative to R290, since it offers the highest COP values for both cooling and heating, and avoids issues related to temperature glide. However, they also affirmed that in systems where compressor size or speed is a limiting factor, mixtures such as RE170/R600/R744 (85/10/5) or (83/9/8) could be a suitable option, as they provide similar performance with slightly lower compressor speed.
Their findings were presented in “RE170 (Dimethyl Ether) and ternary mixtures (R744 / RE170 / R600) as alternatives to R290 for refrigeration and heat pump applications,” published in the International Journal of Refrigeration.
Popular content
Global PV dataset shows 2019-2022 data
A research team from China’s Beijing Normal University has developed a novel method for the identification of PV panels worldwide and has created a global database for the years 2019-2022.
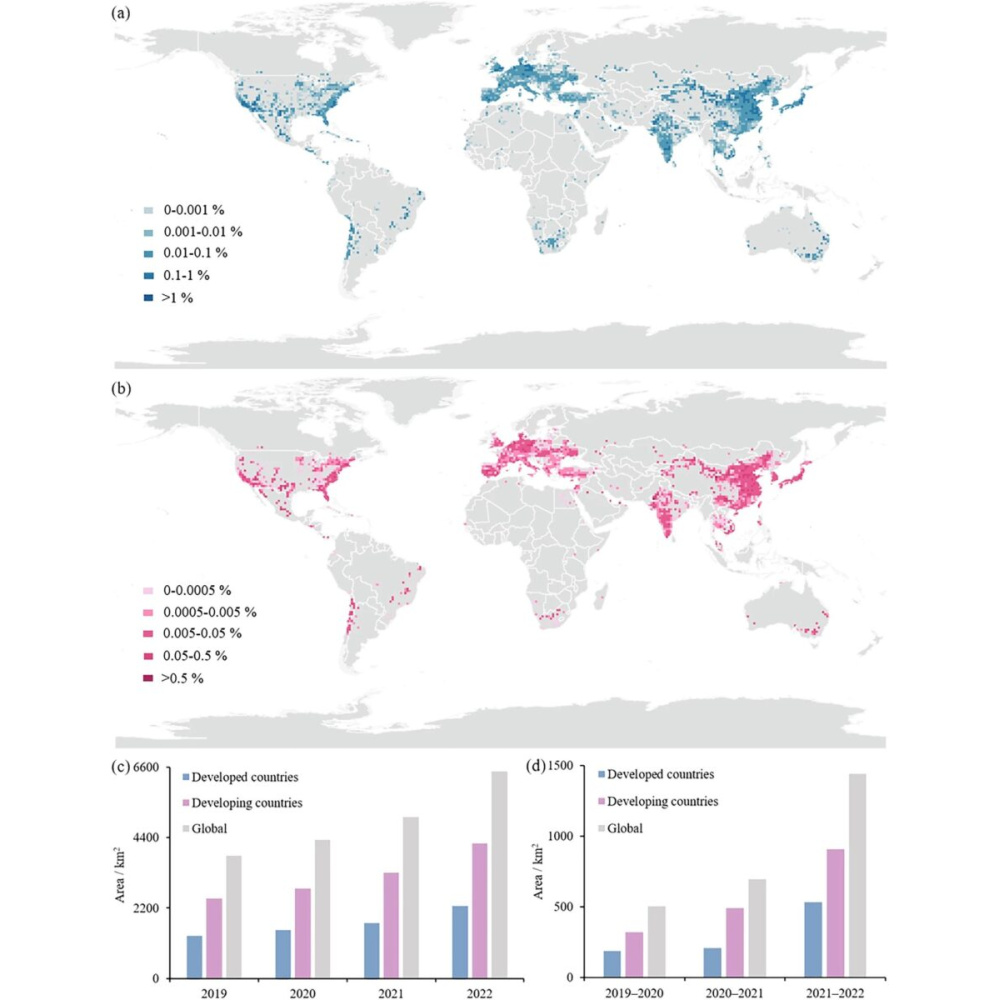
Overall, in 2022, there were 6,469.8 km2 of solar panels worldwide, a growth of more than 60% compared to 2019’s 3,831.6 km2.
“This dataset offers unprecedented detail and accuracy for future research and policy-making,” said the academics. “Our approach is based on the concept of utilizing multi-source remote sensing data and multiple classifiers. It aims to overcome issues such as the difficulty of sample selection in PV extraction, the inefficiency of recognition methods, and the lack of timeliness in existing PV power station datasets.”
To create the dataset, the team has utilized both machine learning and deep learning. The first step in their approach included the deep learning model U-Net, for its ability to find shapes and details. They fed this model with 179 annotated high-resolution pictures from Google Earth (GE). With those, the model was trained to understand how PV sites look before an additional 1,326 images were fed into it. In those, the model had found PV panels.
The PV samples from the first step were then used as examples for the machine learning method, positive-unlabelled learning (PUL)-random forest (RA). The PUL part of this method trains the system on the basis of known positive examples only, while its RA group uses decision trees to vote whether a spot in an image has PV panels. The PUL-RA was then used on images from the Sentinel-2, covering the entire plant. Each place on earth is captured in the resolution of two months.
Comparing the accuracy of the new PV dataset from 2019 to 2022 with Kruitwagen’s dataset, the accuracy of the new dataset is over 90%, which is slightly higher than the dataset provided by Kruitwagen,” the team said. “The PV extraction method proposed in this study has high accuracy and stability on the validation set from 2019 to 2022, which implies that the two-stage classification framework can extract PV efficiently, and likewise indicates that the production of the new global PV dataset from 2019 to 2022 is reliable.”
Per their measurements, the global PV area in 2019 was 3,831.6 km2, while in 2020 it stood at 4,334.4 km2, in 2021 at 5,030.3 km2, and in 6,469.8 km2 in 2022. China is the country with the most significant amount of PV and the most considerable amount of PV growth, with a PV area of 2,542.5 km2 and a growth of 1,014.6 km2 by 2022. The US came second in the 2022 size list, with 1,051.4 km2, India came third with 673.9 km2, and Germany fourth with 248.1 km2.
“Statistics on the area and change of PV solar panels in developed and developing countries from 2019-2022 show that the PV area in developing countries is much larger than that in developed countries,” the academics added. “As of 2022, developing countries own 4,211.2 km2 of PV, which is about twice as much as developed countries, and the amount of new PV in developing countries is also higher than that in developed countries, with the new PV area in developing countries being 1,713.3 km2. From this observation, PV in developing countries is ahead of that in developed countries, and it is the mainstay of the world’s PV market.”
The annual global PV dataset is publicly hosted online. Details about it appeared in “Global photovoltaic solar panel dataset from 2019 to 2022,” published in Scientific Data. Scientists from China’s Beijing Normal University and the Moganshan Geospatial Information Laboratory have participated in the study.
Popular content
Bali launches rooftop solar acceleration program

The Indonesian province of Bali has launched a program to accelerate the deployment of rooftop solar systems.
The flagship initiative launched by Bali Governor I Wayan Koster aims to boost rooftop solar installations, focusing on government buildings, public facilities, and the business sector.
At the program’s launch, Koster said all provincial, district, and city government offices must use rooftop solar, along with all hotels, villas, schools, campuses, and markets.
The Institute for Essential Services Reform (IESR), a Jakarta-based think tank, has welcomed the program, calling it a “fast, flexible solution that fits the geographical conditions and socioeconomic structure of Bali.”
The province’s total solar potential is 22 GW, with rooftop solar potential estimated at 3.3 GW to 10.9 GW, according to analysis by IESR. To date, Bali has utilized just 1% of that capacity and remains heavily reliant on fossil-based electricity.
IESR Executive Director Fabby Tumiwa said large-scale, distributed rooftop solar systems should include battery energy storage systems (BESS) to reduce the risk of supply failures from Java, which currently provides 25% to 30% of Bali’s electricity via interconnection cables.
The think tank also urged the Indonesian government to revoke the current quota system and reintroduce net-metering, along with support for rooftop solar paired with BESS for commercial and industrial buildings.
The institute added that, as the center of culture and tourism in Indonesia, Bali can serve as “a real example of a just and community-based energy transition.”
“Rooftop PV is not only a technical solution, but also a symbol of citizen participation in saving the earth,” the think tank said. “To realize this, IESR encourages the expansion of collaboration between local governments, [government-owned utility] PLN, educational institutions, local communities, businesses, and civil society organizations.”
Bali has set a target of reaching net zero emissions by 2045, while Indonesia is targeting decarbonization of its energy system by 2060 or earlier. The nation‘s cumulative solar capacity surpassed 700 MW in August 2024, according to figures from IESR.
Popular content
European electricity prices rise despite negative weekend values
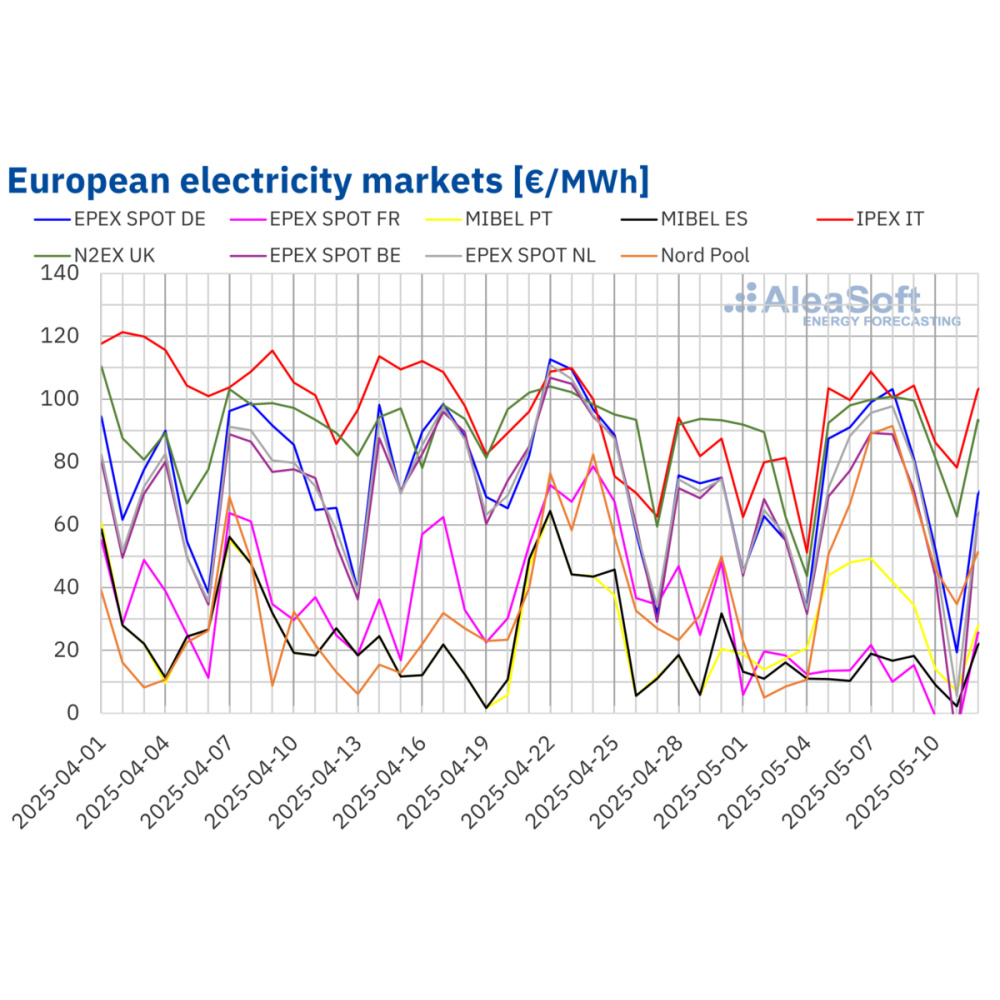
Most major European markets experienced an upswing in the average electricity price during the second week of May, according to analysis from AleaSoft Energy Forecasting.
When compared to the week prior, the consultancy noted an increase in the weekly average electricity price in the Belgian, British, Dutch, German, Italian, Nordic and Portuguese markets. Averages were above €60 ($67.24)/MWh in most cases, with the Italian market having the highest average, at €97.25/MWh.
AleaSoft attributed the price hikes to an increase in the weekly price of gas and CO2 emission allowances and a rise in electricity demand in most countries.
The French and Spanish markets bucked the upward trend, with average electricity prices falling to the lowest recorded figures of the week, at €9.61/MWh and €12.35/MWh. AleaSoft said a significant increase in wind energy production in France and solar energy production in Spain led to these lower prices.
On Sunday, May 11, most analyzed markets recorded negative hourly prices. The German, Dutch and Belgian markets reached the lowest hourly prices of the week, at -€250.32/MWh, -€350.00/MWh and -€462.33/MWh. This was the lowest hourly price in the Belgian market since June 2019 and the lowest in the German and Dutch markets since July 2023. On the same day, the Spanish market recorded its historical minimum hourly price, reaching -€15.00/MWh between 16:00 and 17:00.
May 11 also saw the French and Belgian markets record negative daily prices, of -€5.84/MWh and -€9.97/MWh. This was the lowest daily price in France since May 2020.
AleaSoft is predicting the third week of May will bring similar electricity prices to this week across most analyzed markets, but an increase in prices is expected in France and Spain.
The consultancy also found solar energy production rose week-on-week in Germany, Portugal and Spain last week but fell in France and Italy. On May 6, Portugal produced 26 GWh of solar, an all-time daily record for the country.
AleaSoft is predicting solar energy will have increased in Germany this week but will have continued to decline in Italy.
Popular content
Biwatt launches commercial sodium-ion energy storage product

From ESS News
Chinese energy storage manufacturer Biwatt has introduced a C&I product based on sodium-ion cells. The Powerlake I2 is said to be safer than rival energy storage systems because its cells are thermally inert – meaning they won’t self-ignite.
The Powerlake I2 is an all-in-one system with energy storage and an inverter housed in a single control cabinet. Operation is designed to remain stable even under extreme temperature conditions – from -30 C to 55 C.
In the event of a power outage, the system can switch to off-grid operation in less than 20 milliseconds, ensuring uninterrupted power supply.
Popular content
Tender opens for hybrid solar systems at Sudanese refugee camps
The UNHCR is administering a tender for the provision of solar hybrid systems for five water treatment plants at refugee camps in White Nile State, Sudan.
The chosen applicant will be responsible for the engineering, procurement, construction, delivery, installation, testing and commissioning of the five hybrid systems, alongside a two-year operations and maintenance contract.
The tender details state that the hybrid system will include a solar array, hybrid inverter, battery, surface water pump, and diesel generator.
The prospective applicants must have a minimum of five years of experience working with PV solutions of a minimum 55 kWp and an accumulative capacity of at least 275 kWp of solar projects.
To confirm participation, interested bidders are asked to submit a letter of intention to bid by May 20. A non-mandatory pre-bid site visit is taking place from May 20 to 23. The deadline for expressions of interest is May 30.
Popular content
Austria records 20% decline in PV capacity expansion in first quarter

According to initial industry estimates, Austria's photovoltaic capacity expansion in the first quarter of 2025 fell by approximately 20% compared to the same period last year, photovoltaic association PV Austria announced on Wednesday.
According to a report published by E-Control, 497 MW of photovoltaic capacity were added in the first three months of the previous year. However, a downward trend in demand was already evident towards the end of the year. Overall, PV capacity expansion in 2024, at 2.2 GW of newly installed capacity, fell short of the almost 2.5 GW in 2023.
The reasons for this development are not difficult to identify, according to PV Austria. “While the government program invokes the goal of ‘affordable energy' more than 20 times, the same government has been dealing the domestic renewable energy industry one blow after another since taking office,” it stated. The new government took office in March 2025 and immediately decided to end the VAT exemption for small photovoltaic systems, which was originally supposed to remain in effect until the end of the year. The government's argument that it wanted to use the funds to balance the budget was based on “dubious estimates of the additional tax revenue that could be achieved,” the association said. At the same time, the government also extended and tightened the so-called Energy Crisis Contribution for Electricity (EKB-S). According to PV Austria, this particularly affects domestic, medium-sized electricity producers. In addition, there are cuts to all environmental subsidies.
“Instead of using the growing renewable energy sector to generate additional funds for budget consolidation, successful companies are being penalized,” said Herbert Paierl, CEO of PV Austria. “Those who choke off PV and storage companies today will import unemployment tomorrow and overpriced electricity from abroad the day after.”
The association also called on the government to finally pass the new Electricity Industry Act (ElWG) and the Renewable Energy Expansion Acceleration Act (EABG). Both projects are essential to legally advance the restructuring of the energy system and to provide affordable energy. This does not require additional funding from the state budget; it is simply a matter of creating legal guardrails. “If the industry is already confronted with drastic budget cuts and planning security is being taken away, at least the announced laws must be passed before the summer,” Paierl said.
Confidence in stable framework conditions is currently eroding rapidly. Projects are already being halted and financing is becoming more expensive. Against this backdrop, PV Austria warned that the goal of affordable energy cannot be achieved in this way and that this will also have serious consequences for the Austrian industry. Thousands of jobs will be lost, and it represents a “setback as a location for innovation for green technologies.” The government is missing the opportunity to balance its budget through real growth and not just through new taxes and levies, PV Austria stated.